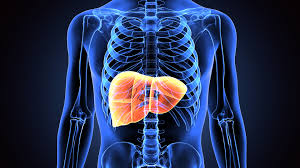
Liver cancer originating from liver cells can be primary liver cancer which begins in the liver or secondary liver cancer that started in another part of the body but has spread to the liver.
Primary liver cancers are uncommon and but the numbers are increasing over years. There are different types:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or Hepatoma, is the most common type of primary liver cancer and it starts in the main cell type in the liver, the hepatocytes
- Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, starts in the cells lining the bile ducts (which connect the liver to the bowel and gall bladder)
- Angiosarcoma, which starts in the blood vessels. This is a rare type of liver cancer that is more likely to occur in people over 70.
The symptoms of liver cancer are more likely to appear as the cancer grows or becomes advanced. Symptoms may include weakness and tiredness, pain in the right side of abdomen, swelling of the abdomen due to a build-up of fluid (ascites), pain in the right shoulder, loss of appetite loss and weight loss, yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) and fever.
The most important causes of liver cancer is long standing infection of Hepatitis B or C viruses. Other risk factors are fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes, alcohol consumption, obesity, genetic disorders including haemochromatosis, or alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency and exposure to certain chemicals.
Diagnostic tests include blood tests like liver function test, tumor markers like AFP, Ca 19.9 , tests for hepatitis B or C infection Ultrasound, triple phase CT or MRI scan, PET-CT scan and biopsy.
Treatment of liver cancer is a team effort and is based on a number of factors like stage, size, location of tumor and condition of the remaining healthy liver. It involves combined decision making by the hepatobiliary surgeons, gastroenterologist, hepatologist, radiation oncologist, medical oncologist and intervention radiologist.
Treatment may vary from surgical resection with removal of the diseased liver to liver transplant. Other options are tumour ablation treatments using radio waves and microwaves to heat and destroy cancer cells. Radioembolisation (TARE ) targets liver tumours directly with high doses of internal radiation in tiny beads. Sterotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is an advanced technique of delivering radation precisely and accurately directed to the tumor without damaging the surrounding healthy liver.
Chemotherapy given systemically, via tablets or intravenously can be used to kill the cancer cells or slow down their growth or prevent regrowth. It can also be given directly into the tumour, which is called chemoembolisation (or TACE).
Biological therapy work against the cancer cells by either stopping their growth or function, or by helping the body’s immune system destroy them. Palliative care aims to improve your quality of life by alleviating symptoms of cancer in advanced stages of cancer. It may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy or other drug therapies.
It is important to emphasize that liver cancers are one of the deadliest cancers but are easily preventable by vaccinating against Hepatitis B virus. Maintaining a healthy life style with healthy body weight and abstinence from alcohol can also prevent liver cancer.